ERP software is one of the world's leading business management software in terms of efficiency. So what is ERP management software? What role and benefits does this software have for businesses? Let's find the answer with ERPToancau.
ERP concept: ERP software (Enterprise resource planning software), abbreviated as ERP, is a software solution that supports the business management process of an enterprise. The main function of ERP is to integrate all information and data of departments into a single computer system for monitoring, fully meeting the needs of the business, and quite flexible to use. You can imagine using ERP like a giant software system, solving problems of human resources, finance, production, supply chain, warehouse, purchasing, sales and many other things.

2. History of ERP formation
History of the birth of ERP
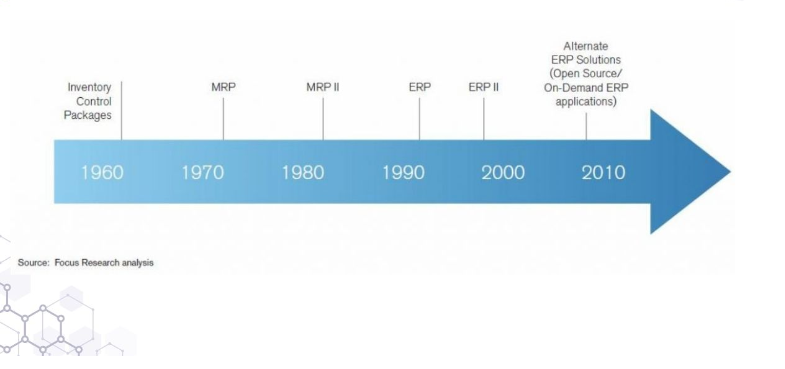
During the 1960s, J.I. Case - a tractor and construction machinery manufacturer - collaborated with IBM to develop the first material requirements planning (MRP) system, marking the birth of ERP. While MRP systems were initially expensive to build, required a team of experts to maintain and took up a lot of space, these MRP systems have helped manufacturers manage raw material procurement and product deliveries. products to the factory for better production planning.
Although the technology gained traction in the 1970s, it was still limited to large companies with the budget and resources for internal development. To this end, major software companies such as Oracle and JD Edwards have aimed to develop ERP software that is accessible to more businesses. This has helped businesses optimize production processes, manage resources and improve their business efficiency.
Development history of ERP
In 1990, research company Gartner introduced ERP by coining the term "enterprise resource planning". To demonstrate the use of technology in enhancing the overall efficiency of businesses, not just in the manufacturing sector. One of the typical examples of this development is the ERP system, which is characterized by a unified database for all company information. ERP systems provide various business functions, including accounting, sales, engineering and human resources, to ensure accuracy and reliability for all employees.
During the 1960s, J.I. Case - a tractor and construction machinery manufacturer - collaborated with IBM to develop the first material requirements planning (MRP) system, marking the birth of ERP. While MRP systems were initially expensive to build, required a team of experts to maintain and took up a lot of space, these MRP systems have helped manufacturers manage raw material procurement and product deliveries. products to the factory for better production planning.
Although the technology gained traction in the 1970s, it was still limited to large companies with the budget and resources for internal development. To this end, major software companies such as Oracle and JD Edwards have aimed to develop ERP software that is accessible to more businesses. This has helped businesses optimize production processes, manage resources and improve their business efficiency.
Development history of ERP
In 1990, research company Gartner introduced ERP by coining the term "enterprise resource planning". To demonstrate the use of technology in enhancing the overall efficiency of businesses, not just in the manufacturing sector. One of the typical examples of this development is the ERP system, which is characterized by a unified database for all company information. ERP systems provide various business functions, including accounting, sales, engineering and human resources, to ensure accuracy and reliability for all employees.
During the 90s, ERP systems continued to be developed and advanced significantly as cloud ERP was first introduced in 1998 by NetSuite. Cloud ERP allows businesses to access critical business data over the internet from any device, minimizing the need for hardware and IT staff, leading to easier deployment and helps SMEs access the same solutions as their larger counterparts.
In 2000, Gartner introduced the idea of ERP II to refer to internet-enabled systems that can pull data from different sources, including office applications such as customer relationship management, e-commerce , marketing automation, supply chain management and human resource management. This is a significant step forward to help take advantage of opportunities for improvement and solve problems in the ERP system.
Today, leading ERP software is capable of generating vast information stores and providing reports that help improve the performance of the entire business, from sales and marketing to product development and operations. personnel.
3. What benefits does ERP management software bring to businesses?
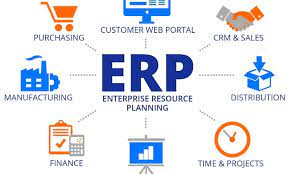
Overview of ERP is a powerful assistant for businesses that want to increase orders, control customers, production efficiency, inventory, etc. Here are some benefits of ERP systems:
Control customer information: customer information will be shared with departments that need it such as customer care, sales, accounting, etc. A senior director sitting in the office can control Get all customer information in real time, know how many products the customer has purchased, how much money they have spent and at which store system of the business.
Speed up the production and provision of goods and services: ERP with support features can help reduce manual work by automating part or all of the process. ERP automation is most effectively applied to production processes, packaging, and output management.
This helps businesses improve the production process, save time for products to reach consumers, and reduce labor costs and storage costs.
Quality inspection and project management: The ERP system will help businesses check and monitor product quality, while helping businesses plan and allocate resources appropriately. With ERP management software, businesses can understand the entire workload that project members are doing, thereby automatically assigning capable members to the most suitable jobs.
Control financial information: ERP software will automatically synthesize information from departments according to accounting requirements, ensuring accurate data and limiting errors. ERP can also support the creation of financial reports according to international standards.
Inventory control: With ERP software, you will always know the inventory situation, location, and number of stores. This makes it easier for managers to make decisions, plan, enter data or suggest additional options to push old inventory out of the warehouse. Thanks to ERP, working time will be reduced, fewer personnel will be needed, but the efficiency and working speed of each employee will increase.
Standardize human resource activities: through ERP management software, each individual's working hours, home hours, and workload are effectively controlled, regardless of which department that individual works in. This will help managers evaluate employee capabilities, reward and punish fairly, and pay salaries on time.
4. Types of ERP software
ERP software can be classified in many different ways. Here are some common classifications of ERP software:
Based on scale
ERP software for Small and Medium Enterprises: Specifically designed for small and medium-sized businesses with smaller operating scales and simpler management needs.
Phần mềm ERP cho Doanh nghiệp lớn: Dành cho các doanh nghiệp lớn có quy mô hoạt động lớn, yêu cầu phức tạp và tích hợp nhiều hệ thống và quy trình.
Based on industry
Specialized ERP Software: Provides customized ERP solutions for specific industries such as manufacturing, retail, financial services, healthcare, tourism, and more.
Industry-wide ERP software: Suitable for businesses operating in many different industries that do not require high specialization.
Based on specific functions
Finance: Focus on financial management, accounting, budget control and financial reporting.
Supply chain: Manage the entire supply chain, from sourcing to manufacturing, storage, distribution and transportation.
Customer management (CRM): Focuses on customer information management, customer relationships and sales.
Human resource management (HRM): Manage employee information, recruitment process, salary management and welfare regimes.
Platform-based
Cloud ERP software: Provides ERP services over the internet, allowing remote access and more flexibility.
On-premise ERP software: Is a traditional model in which the software is deployed and installed on-site. Businesses have complete control over this process. You can install the software anywhere in your data center. Responsibility for software installation and hardware maintenance is assumed by the employees of the business or organization.
If in the past, traditional ERP management software (deployed on the enterprise's own server) was more popular, now, with the rapid development of information technology, Cloud ERP (stored ERP Cloud storage) are increasingly being used because of their convenience and cost savings.
5. Basic difference of ERP compared to many discrete management software
The basic difference of ERP management software compared to many discrete software is the ability to integrate. ERP is a single software system, its modules have similar functions to discrete software, but they do much more thanks to integration capabilities. In the ERP system, modules are closely related to each other like parts on the same human body. Therefore, information is shared immediately from one department to another, ensuring accuracy and speed.
Discrete software often only serves the operations of a specific department and is like an oasis for other departments' software. Information circulation is done manually with low productivity, lack of control and is prone to errors. With ERP, information is easily circulated according to processes and strictly controlled. ERP management software can synthesize information from many departments to produce the most accurate summary report. In this way, labor productivity and information management efficiency will be increased.
Above is an overview of ERP software that leaders need to know. With experience in successfully implementing many ERP projects for small and medium-sized businesses, ERPToancau is always ready to help, advise and troubleshoot all your business's problems related to implementing effective ERP management software. fruit.
Address: 16/117 Nguyen Son, Gia Thuy Ward, Long Bien District, Hanoi, Vietnam
Phone: +(084)943730142
Email: erptoancau@gmail.com
Website: https://erptoancau.com